To maintain energy and stay healthy, your diet should provide essential micronutrients like vitamins and minerals. It should also include macronutrients such as proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. This blog introduces a balanced variation. It includes small amounts of quality carbohydrates to support daily energy needs. This approach does not disrupt fat metabolism. We will focus on nutrient-dense whole foods that support sustained energy and optimal health.

Why Nutrient-Dense Foods Matter?
- Micronutrients: Essential for boosting immunity, enhancing energy production, and promoting overall well-being.
- Macronutrients: The vital source of energy and building blocks your body requires for optimal functioning.
- Grain-Free Advantage: Steering clear of grains and refined carbs helps:
- Prevent blood sugar spikes
- Promote gut health
- Support long-lasting energy levels
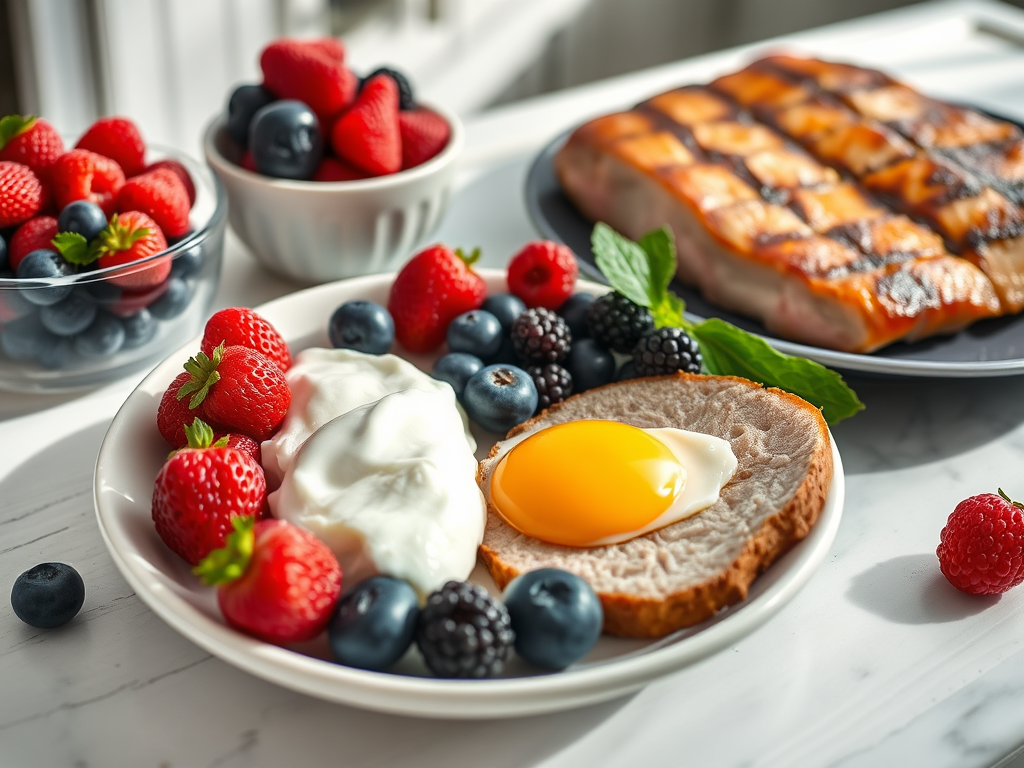

Core Principles of a Balanced Diet
- Emphasize Healthy Fats (50-60% of Daily Calories)– Why?: Fats provide a steady energy source and are essential for brain health, hormone production, and cell function.
- Best Source Of Fats –
- Avocado
- Coconut Oil
- Ghee (Clarified Butter)
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- Nuts (Almonds, Macadamia Nuts, Walnuts, Pecans)
- Fatty Fish (Salmon, Sardine, Mackerei)
- Butter
- Best Source Of Fats –
- Focus on High-Quality Proteins (25-30%) – Protein is essential for muscle repair, immune function, and maintaining metabolic health.
- Best Sources Of Protein
- Free – Range Eggs
- Organic Chicken & Turkey
- Wild Caught Fish
- Organic Lamb & Beef
- Indian Cheese
- Parmesan & Gouda Cheese
- Full Fat Dairy Products
- Whey Protein Isolate (Check Labels to Avoid Any Preservatives & Sugar)
- Best Sources Of Protein
- Include Fiber-Rich, Low-Carbs Vegetables (10-15%) – Non-starchy vegetables provide vital vitamins, minerals, and fiber without the blood sugar spikes.
- Best Sources
- Leafy Green Vegetables (Spinach, Arugula, Celery)
- Cruciferous Vegetables (Cabbage, Broccoli, Brussels Sprouts, Bok Choy)
- Zucchini, Mushroom, Lady Fingers, Asparagus
- Bell Pepper & Cucumber
- Ginger, Garlic, Onion & Lemon
- Best Sources
- Incorporate Natural Carbs Source In Moderation – Include whole food source of carbs. this will support post/pre workout energy levels without the needs of refined grains or carbs.
- Best Source Of Carbs
- Sweet Potatoes
- Pumpkin
- Beets
- Berries (Blueberries, Raspberries & Strawberries)
- Best Source Of Carbs

Essential Micronutrients to Include
- Vitamin C – Bell Pepper, Citrus Fruits & Broccoli.
- Magnesium – Spinach, Nuts, Dark Chocolate (80% or above).
- Vitamin D – Sunlight, Fatty Fish & Egg Yolk.
- Potassium – Avocado, Leafy Greens, Sweet Potato, Pumpkin.
- Iron – Red Meat, Spinach & Pumpkin Seeds.

Sample Of 1 day Meal Plan
- Breakfast – 2 eggs Or 150 g of Indian Cheese + A side of sauteed mushrooms + 1/2 Avocado.
- Snack – Mix of Nuts ( Pecan & Macadamia Nuts as they are low in calories).
- Lunch – Grilled Salmon or Chicken Roasted with Spinach Or A mixed greens salad with olive oil and lemon dressing.
- Snack – A cucumber with guacamole dip Or 1 scoop of Whey Isolate.
- Dinner – Grass Fed Chicken/beef/lamb/Indian cheese + Mashed cauliflower with season herbs & spices + Steam Broccoli.
- Snack (optional) – Fresh berries with coconut cream.

Why This Works?
- Steady Energy: Healthy fats and protein prevent energy crashes, while low-carbs vegetables and natural carbs provide fiber and micronutrients.
- Improved Digestion: Avoiding grains supports gut health, reducing bloating and inflammation.
- Nutritional Density: Whole foods pack essential nutrients without the empty calories of refined carbs.

- Meal Prep: Keep your fridge stocked with pre-washed veggies, cooked proteins, and ready-to-eat snacks.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water and consider adding electrolytes to maintain balance.
- Listen to Your Body: Adjust portions of fats, proteins, and carbs based on your energy demands and activity levels.
Empower Your Health – Fuel your body with whole, nutrient-rich foods for peak performance. This powerful nutrition strategy keeps you energized all day long, promotes lasting health, and fosters sustainability. Discover the flexibility that makes it easy to maintain your commitment in the long run.
What are your favorite meals? Share your ideas and tips in the comments below!